Collisions
Brakeza3D provides flexible collision modes and shapes, allowing developers to detect collisions, respond to physical interactions, and apply custom gameplay logic through LUA scripts.
All object instances can participate in the collision system, supporting ghost, rigid body, and kinematic behaviors depending on the configured mode.
From the menu, you can configure fundamental aspects such as gravity strength and various performance settings:
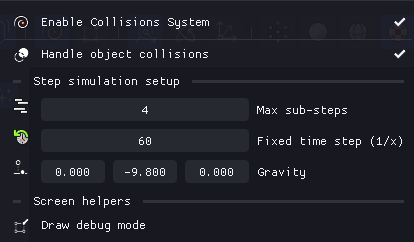
Collision Modes
| Mode | Physics Reaction | Typical Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Ghost | No physical response | Triggers, sensors, detection zones |
| RigidBody | Reacts to forces, collisions, gravity | Realistic physics objects, falling items |
| Kinematic | Controlled by code, not physics | Player characters, moving platforms |
Ghost Mode
Detects collisions but is not affected by them. Ideal for trigger zones that activate events when the player enters.
RigidBody Mode
Fully simulated physics object. Can be set as static (mass = 0) for immovable obstacles. This is the only mode allowed for non-convex geometries (triangle mesh).
Kinematic Mode
Movement is controlled manually via code methods. The physics engine handles collision detection but not movement forces. Perfect for player characters that need precise control.
Collider Shapes
| Shape | Performance | Typical Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Simple Shape | Excellent | General-purpose objects, boxes, spheres |
| Capsule Shape | Good | Characters, tall or rounded objects |
| Triangle Mesh | Lower | Static meshes requiring precise collisions |
- Simple Shape: Basic convex hull, fastest performance
- Capsule Shape: Pill-shaped collider, great for characters
- Triangle Mesh: Matches exact geometry, use only when precision is critical
Collider shapes can be configured either through the GUI or via LUA scripts.
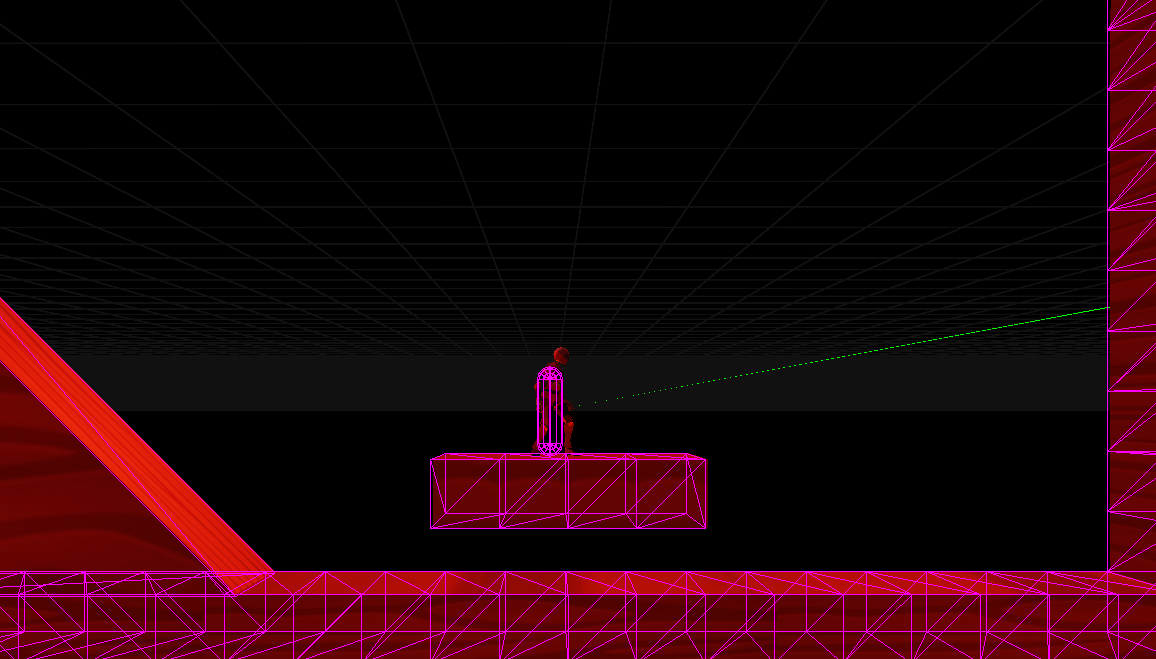
Debug Collisions
You can debug the collision system both visually and through system logs:
- Visual debugging: Display collision shapes and boundaries directly in the scene
- System logs: Runtime information about collision events and interactions
This helps identify incorrect alignments, unexpected intersections, and fine-tune collision behavior.
Scripting API
For programming collisions via LUA scripts, see the Collision System API reference, which includes:
- Setting up colliders (
setupGhostCollider,SetupRigidBodyCollider) - Applying forces and impulses
- Kinematic movement methods
- Collision callbacks (
onCollision) - Bone mapping for animated models